Graphene is an ultimately thin (one-atom-thick !) material made of pure carbon planar crystal with an in-plane honeycomb atomic structure similar to graphite. Unlike bulk graphite, its purely two-dimensional character gives him exceptional electronic, thermal, optical and mechanical properties. First isolated in 2004 by K. Novoselov and A. Geim at the University of Manchester. They have been awarded the Nobel Prize of Physics in 2010 for their discovery.
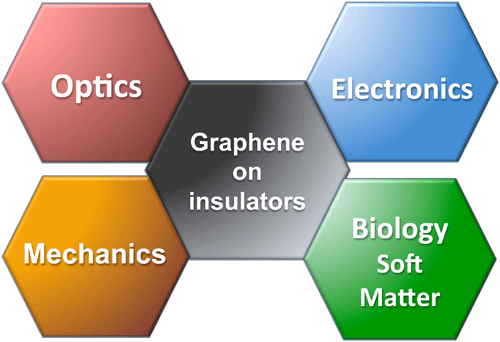
With numerous applications, Graphene on insulator
is a the crossroads of many disciplines such as optics,
electronics, mechanics and biomedecine.
It can be integrated into new classes of electronics devices
bringing together the combined properties of graphene.
Being FLEXIBLE, TRANSPARENT & ELECTRICALLY CONDUCTIVE ,
GRAPHENE
offer a new material for the integration of electronics in a new class of systems
such as :
OPTOELECTRONICS at HIGH FREQUENCIES
FLEXIBLE DISPLAYS ( OLEDs based ,...)
WEARABLE ELECTRONICS